Stamen, Microsporangium and Pollen Grain
Stamen, Microsporangium and Pollen Grain: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Intine, Pollen Grain, Microsporogenesis, Anther, Microsporangium, Pollen Allergy, Tapetum, Sporopollenin, Endothecium, Exine, Germ Pore, Pollen Bank, Filament of Stamen and, Middle Layer of Microsporangium
Important Questions on Stamen, Microsporangium and Pollen Grain
What is microsporangia?
Write a brief note on the following-
Palynology
Write a brief note on the following-
Callose deposition
Write a brief note on the following:
Pollen wall proteins
Write a brief note on the following-
Pollen wall structure
Microsporangium is also known as _____
What is the difference between microsporangia and microsporangium?
Pollen grains of water pollinated species have special characteristics for protection from water is called.
Does tapetum help in dehisence?
How do tapetal cells become bi-nucleate?
Do all flowers contain anther?
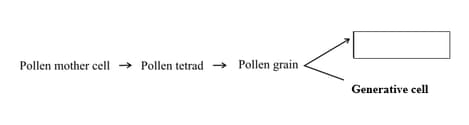
Complete the following chart from the given options
Functions of tapetum include
How many meiotic divisions are required to form 200 pollen grains?
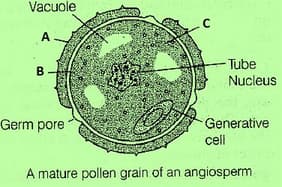
What are the labels A and B indicate in the given picture of a pollen grain?
During pollen germination, intine forms a pollen tube and extrudes out through the germ pore.
Draw the structure of a pollen grain and label the inner layer of the wall of it.
The inner layer of wall surrounding the pollen and spore that protects the reproductive cells is known as _____ (intine/exine).
Exine of pollen helps attachment to _____ (pollinators/stem).
Which of the following feature/s is/are correct about the outermost layer covering the pollen grains?